Neas-Teicneolaíocht Sárphlaisteacha
The research on the superplasticity of the microcrystalline material structure (the average size of the grains usually does not exceed 10 ~ 20μm) is at elevated temperatures and relatively low deformation speed (usually 10-4 ~ 10-3s-1) ongoing. In fact, it has been determined that any polycrystalline material, including industrial alloys such as aluminum-based, titanium-based, and nickel-based, can be transformed into a superplastic state. In many cases, the use of superplasticity in metal pressure processing can ensure lower deformation forces, reduce the number of process steps, and improve the mechanical properties and dimensional accuracy of semi-finished products. Under conventional forging conditions, the forging temperature range of these metal materials is relatively narrow, especially when rolling thin plates, high ribs, and thin-walled parts, the heat of the billet is quickly absorbed by the tool, and the temperature drops rapidly. Not only does it need to greatly increase the tonnage of the equipment, but it is also easy to cause cracking of the tooling. Especially titanium alloy is more obvious, it is very sensitive to deformation temperature, when the deformation temperature drops from 920 ℃ go 820 ℃, tá an friotaíocht dífhoirmithe beagnach dúbailt. Níl an fórsa dífhoirmithe superplastic de chóimhiotal tíotáiniam ach thart ar 1/30 ~ 1/10 de ghnáth-rollta. Úsáidtear cóimhiotail tíotáiniam go forleathan i go leor réimsí tionsclaíocha, lena n-áirítear aeraspáis, feithicleach agus bithleighis. Mar is eol dúinn go léir, tá plaisteacht íseal agus struchtúr míchothrom ag go leor cóimhiotail tíotáiniam sa stát soláthair. Dá bhrí sin, tá tábhacht phráinneach phráinneach ag baint le páirteanna casta saor, ardchaighdeáin a fháil ó na hábhair seo. Ceann de na bealaí éifeachtacha chun an fhadhb seo a réiteach ná teicneolaíocht sárphlaisteach a úsáid. Ar an drochuair, tá sé deacair agus costasach gráin ultrafine a tháirgeadh i gcóimhiotail éagsúla.
Sárphlaisteachas garbhghráin
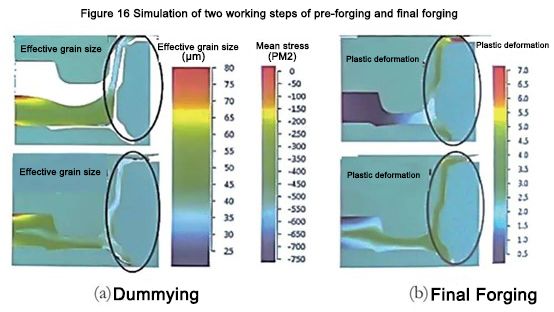
Chomhoibrigh OIВyly а, Р.L.Вlekvell (Strаthсlyde, Ollscoil Shrath Chluaidh Ghlаsgow, an RA), Р.А.Васин (Scoil na hInnealtóireachta Meicniúla, Ollscoil Stáit Mailí, an Rúis), MKSаrаndzhi (Scoil Oideachais agus Taighde Teicneolaíochta Indiach) i gcomhar le chéile ar staidéar a dhéanamh ar shárphlaisteachas garbhghráin. Ceann de na príomhbhuntáistí a bhaineann le foirmiú preas superplastic ná gur féidir leis an ábhar dífhoirmíochtaí an-mhór a bhaint amach. Mar sin féin, ní éilíonn go leor próisis dífhoirmiú 100% go 200%. Go ginearálta, sroicheann an cóimheas brionnú miotail 5, is é sin, sroicheann an dífhoirmiúchán 75%. Ní bhíonn an barr is fearr ag teastáil i gcónaí chun inseirbhísiúlacht ard na gcodanna a chinntiú. Thairis sin, tá cobhsaíocht níos fearr ag an microstructure lamellar garbh i gcoinne iomadú crack tuirse. In order to obtain high-quality blanks, rough-grained material blanks are first used, whose microstructure cannot guarantee the typical superplastic grain boundary slip deformation mechanism. Under this condition, since the sensitivity to deformation rate is lower than the material superplastic condition, the material can be deformed and softened, and the microstructure can be transformed during deformation. Experimental studies have pointed out that this process can be called approximate superplastic deformation, and some parts of the grain are broken, which can reach a relatively high deformation of 100% to 300%. Coarse-grained titanium alloys are used in the hot die forging of automobile wheel hubs. Two-phase (α+β) titanium alloys with flaky (Widmandelsteiner) microstructure have initial broken grains. β-phase about 250 μkm, α-phase flakes The average length is about 21 μkm and the thickness is about 2 μkm. This example simulates the process and analyzes the obtained results, demonstrating the feasibility of approximate superplasticity techniques. Insamhladh próiseas foirmithe roth gluaisteán cóimhiotail tíotáiniam superplaisteach garbh-ghráinneach, mar a thaispeántar i bhFíor 14, ar mhaithe le simplíocht, úsáideann gach insamhalta próisis isothermal (T=900).℃), tá an chomhéifeacht frithchuimilte céanna de 0.5 ag an dromchla teagmhála, agus an toimhde úsáid a bhaint as bealaí gloine. Céimeanna foirmithe sárphlaisteacha garbhghrácha do mhoil rotha gluaisteán ard-deireadh.
Torthaí dífhoirmithe bearnaí garbh-ghráin do rims TC4
From the standpoint of rim deformation, 3 -step die forging is still feasible (Fig. 16). It is not difficult to see that at the end of the third step, the cumulative plastic deformation of this part is 300% to 400%, in some places it exceeds 450%, and in some points, it even exceeds 500%. Although the deformation results showed that the microstructure uniformly changed to 30 to 35 μkm at the end of the second step and to 20 to 25 μkm at the end of the third step, the tensile elongation of the specimen with such a microstructure unexpectedly reached δ=400 %~500%. Is féidir leis an insamhalta ábhair a thaispeáint, i ngach réimse dian dífhoirmithe den bhrionnú, go bhfuil meán-strus an bhrionnú diúltach (faoi choinníoll comhbhrú hidreastatach), is é sin le rá, cuirtear deireadh leis an bhfoinse crack nó le pores, agus tá an fheidhmíocht thar a bheith ard.
Superplasticity íseal-teocht
Tá lucht leanúna inneall aerárthach nua-aimseartha agus lanna comhbhrúiteora déanta go páirteach de shnáithín carbóin. Mar gheall ar an meáchan laghdaithe faoi choinníoll neart struchtúrach agus iontaofacht a chinntiú, tá sé an-iomaíoch le lanna cóimhiotail tíotáiniam. Mar sin féin, is é an laige is mó de lanna snáithíní carbóin ná go bhfuil an toughness tionchair ró-íseal. Sa phróiseas úsáide, tá gaineamh, gairbhéal, agus éin buailte ag an imeall tosaigh, rud a fhágann go mbeidh timpistí móra aerárthaí agus bás. Chun an fhadhb seo a réiteach, tá imeall tosaigh an lann clúdaithe le clúdach cosanta cóimhiotail tíotáiniam ard-neart trí pháirteanna nó gliú a shocrú. Ach is ábhar an-chasta é buataisí cóimhiotail tíotáiniam a mhonarú toisc go bhfuil tras-ranna éagsúla ag na buataisí, lena n-áirítear ballaí tanaí agus tras-ranna treisithe, ceannródaíocha trom. Ina theannta sin, tá cruthanna spásála casta ag an sheath, lena n-áirítear cruthanna cuartha sa treo cothrománach agus cuaire eitleán ingearach.
Dhear agus d'úsáid Corparáid Gáis Tuirbín Neamhfheiriúil Mheiriceá (Chromаlloy Gаs Turbine Corporation USА) an cóimhiotal tíotáiniam Ti-6Аl-4V bán tríthoiseach chun an truaill a mhonarú. Tá an bán meilte chun póca V-chruthach inmheánach a chruthú. Déantar na ballaí taobh a easbhrú ansin i dísle roimh an meaisínithe deiridh. Is é 850 ~ 900 an teocht easbhrúite ℃, agus tá an gás dromchla sáithithe gan gás cosanta. Níl tiús bhalla na coda ach 0.2 go 0.5mm, agus éilíonn déantúsaíocht meaisínithe an-deacair. Ar 27 Samhain, 2018, tionóladh "Comhdháil Bhliantúil Idirnáisiúnta Teicneolaíochta Feithicleach 2018 (11ú) agus 'Searmanas Dámhachtana Gradam Nuálaíochta Teicneolaíochta Feithicleach" i Shanghai go mór. 2018 (11ú) Díríonn Comhdháil Bhliantúil Teicneolaíochta Feithicleach Idirnáisiúnta ar fheithiclí nua fuinnimh, bainistíocht fuinnimh, tiomáint uathrialach, líonrú cliste, agus áiteanna éadroma agus áiteanna eile tionscail, agus é mar aidhm aige malartuithe teicniúla gairmiúla a dhéanamh agus ardán comhroinnte teicneolaíochta ceannródaíoch a thógáil. Tá sé mar aidhm ag an searmanas dámhachtainí "Gradam Nuálaíochta Teicneolaíochta Feithicleach" aitheantas a thabhairt do chruthaitheoirí agus do thionscnóirí na dteicneolaíochtaí chun cinn sa tionscal feithicleach agus páirteanna. Rinne saineolaithe cainte, OEManna gluaisteán intíre agus eachtrannacha agus soláthraithe páirteanna gluaisteán, ionadaithe ó institiúidí taighde ollscoile, ionadaithe ó chomhlachais agus gníomhaireachtaí rialtais, agus ionadaithe na meán malartuithe gairmiúla agus teicniúla domhain le níos mó ná 400 aoi, agus bhí siad ag tnúth le níos fearr i gcomhpháirt. todhchaí le haghaidh taistil.
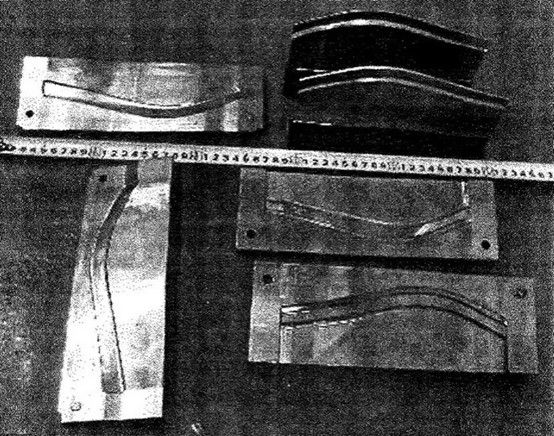
Ba chóir lúbthachta a dhéanamh tar éis coextrusion (Fíor 18).
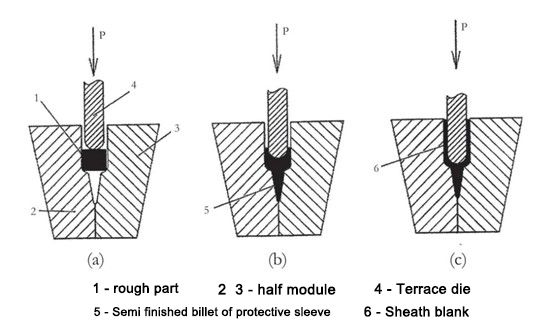
Céimeanna próisis i gcéimeanna éagsúla easbhrúite cumaisc Chun féidearthacht an phróisis easbhrúite ilchodach atá beartaithe a fhíorú, baineadh úsáid as modh insamhalta digiteach. Bunaíodh an próiseas insamhalta ag baint úsáide as na bogearraí Deform 3D, agus bunaíodh an tsamhail ag baint úsáide as na boinn tuisceana bunúsacha:
- tá an bán bunaidh roinnte ina 98000 eilimint chríochta;
- an múnla mar chomhlacht docht;
——The movement speed of the punch is 0.5mm/min;
——The friction between the blank and the mold is set to Coulomb friction, μ=0.2;
——Metal flow under isothermal conditions, blank temperature = 650 ℃;
- Ní bhreathnaítear ar aniseatrópacht nó fiú athchriostalú an bhán le linn an phróisis fhoirmithe.
Fíor 18 Sceitse de chéimeanna lúbthachta
The initial size of the blank: is 5mm × 10mm × 270mm. It is confirmed that the blank material adopts the titanium alloy Ti-6Аl-4V with rheological characteristics collected from this database.
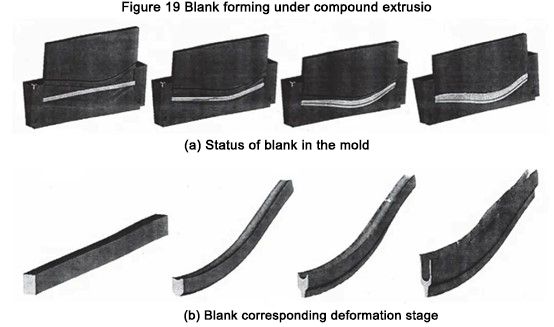
Taispeánann Figiúr 19 staid an bhán nuair a dhéantar é a dhífhoirmiú sa mhúnla agus na híomhánna foirmithe céime comhfhreagracha.

Fíor 19 Foirmiú bán faoi easbhrúite cumaiscn
The simulation results show that the proposed process is feasible, the wall is formed uniformly, and the logarithmic deformation degree at the wall reaches e ≈ 3. The recommended process is effective at temperatures not exceeding 700°C, which reduces the cost of manufacturing mold parts.
We know that titanium alloys including TC4 (Ti-6Аl-4V) in the ultrafine grain state affect the low-temperature superplasticity effect. The preparation of the ultra-fine grain structure of the blank includes the use of a bar with a diameter of φ70mm, changing the axial load, upsetting several times under the condition of gradually reducing the temperature, and then rolling at 600 °C to a thickness of 5mm. The degree of logarithmic deformation e ≈ 3. Deformation results The average grain size is 0.5 μm (Figure 20).
Fíor 20 Micreastruchtúr an bhána
Is é 650 ~ 950 an teocht cóimhiotail tíotáiniam atá beartaithe ℃, agus glacann an próiseas próiseála brú an sciath lipéad ábhair seo a leanas: cuir bealadh gloine FR-6 i bhfeidhm ar an bán bunaidh 1. Cosnaíonn na bratuithe seo i gcoinne ocsaídiúcháin agus saturation gáis agus fiú na hairíonna meicniúla atá beartaithe don mheaisínithe san Argón a bhaint amach. Dá bhrí sin, moltar sciath a chur i bhfeidhm mar ábhar bealaithe sa phróiseas easbhrúite ina bhfuil an bán i dteagmháil leis an dísle. Tá cuair ag cruth an sheath sa phlána cothrománach agus lúbann sé sa phlána ingearach, agus ní mór é a dhíreachú sna plánaí comhfhreagracha roimh easbhrúite. Faoi choinníoll plána cothrománach tugtha, leagtar an bán sa dá leath den dísle le haghaidh easbhrúite. Dún na leatha dísle chun an bán a mhúnlú go dtí an cruth atá ag teastáil agus bain úsáid as punch U-chruthach le haghaidh easbhrúite chun cinn agus droim ar ais. Ansin, athraigh an múnla chun an chéim lúbthachta a bhaint amach le punch V-chruthach. All forming processes are completed on a CNC isothermal forging hydraulic press, and its main technical parameters are: the nominal force of 25MN, with a pressure of 680kN, completed at 650°C, and a deformation speed of 0.5mm/min. The mold material is tool steel 5Cr3W3MoVSi, and the mold is shown in Figure 21. Tar éis easbhrúite cumaisc, comhlíonann na gaibhneachta na ceanglais líníochta. Níl aon lochtanna fillte agus ceapaire i gcuma. Le linn an insamhalta, níor breathnaíodh aon saobhadh balla. Taispeántar an chuid meaisínithe i bhFíor 22. The original structure of the blank is severely deformed (e ≈ 3), which makes it have an ultra-fine grain structure and reduces the process temperature. The microstructure of the sample cut from the wall and front of the sheath is shown in Figure 23. The average grain size of the forgings was determined to be 0.3-0.5μm by a semi-transparent electron microscope. The grain size was reduced to 0.3 μm, and the metal of the wall was severely plastically deformed under the condition of back extrusion. The energy is stored and the grain size is reduced so that the strength of the material is increased by 20% to 30%, and various performance indicators meet the actual requirements. The simulation and test results prove that the trial mass production of sheath parts can be implemented.