대략적인 슈퍼플라스틱 기술
The research on the superplasticity of the microcrystalline material structure (the average size of the grains usually does not exceed 10 ~ 20μm) is at elevated temperatures and relatively low deformation speed (usually 10-4 ~ 10-3s-1) ongoing. In fact, it has been determined that any polycrystalline material, including industrial alloys such as aluminum-based, titanium-based, and nickel-based, can be transformed into a superplastic state. In many cases, the use of superplasticity in metal pressure processing can ensure lower deformation forces, reduce the number of process steps, and improve the mechanical properties and dimensional accuracy of semi-finished products. Under conventional forging conditions, the forging temperature range of these metal materials is relatively narrow, especially when rolling thin plates, high ribs, and thin-walled parts, the heat of the billet is quickly absorbed by the tool, and the temperature drops rapidly. Not only does it need to greatly increase the tonnage of the equipment, but it is also easy to cause cracking of the tooling. Especially titanium alloy is more obvious, it is very sensitive to deformation temperature, when the deformation temperature drops from 920 ℃ 820까지 ℃, 변형 저항은 거의 두 배입니다. 티타늄 합금의 초소성 변형력은 일반 압연의 약 1/30 ~ 1/10에 불과합니다. 티타늄 합금은 항공 우주, 자동차 및 생물 의학을 포함한 많은 산업 분야에서 널리 사용됩니다. 우리 모두 알다시피, 많은 티타늄 합금은 공급 상태에서 가소성이 낮고 구조가 고르지 않습니다. 따라서 이러한 재료로부터 저렴하고 고품질의 복잡한 부품을 얻는 것이 시급한 실질적인 의미가 있습니다. 이 문제를 해결하는 효과적인 방법 중 하나는 슈퍼플라스틱 기술을 사용하는 것입니다. 불행하게도 다양한 합금으로 초미립자를 생산하는 것은 어렵고 비용이 많이 듭니다.
거친 입자의 초가소성
OIВyly а, Р.L.Вlekvell(Strаthсlyde, 영국 스트라스 클라이드 글래스고 대학교), Р.А.Васин(러시아 말리 주립 대학교 기계 공학부), MKSаrаndzhi(인도 교육 연구 기술 학교) 거친 입자의 초가소성에 대한 연구. 초소성 프레스 성형의 주요 이점 중 하나는 재료가 매우 큰 변형을 달성할 수 있다는 것입니다. 그러나 많은 공정에서 100%에서 200%의 변형이 필요하지 않습니다. 일반적으로 금속 단조 비율은 5에 도달합니다. 즉, 변형이 75%에 도달합니다. 부품의 높은 서비스 가능성을 보장하기 위해 최적이 항상 필요한 것은 아닙니다. 또한 거친 라멜라 미세 구조는 피로 균열 전파에 대한 안정성이 더 좋습니다. In order to obtain high-quality blanks, rough-grained material blanks are first used, whose microstructure cannot guarantee the typical superplastic grain boundary slip deformation mechanism. Under this condition, since the sensitivity to deformation rate is lower than the material superplastic condition, the material can be deformed and softened, and the microstructure can be transformed during deformation. Experimental studies have pointed out that this process can be called approximate superplastic deformation, and some parts of the grain are broken, which can reach a relatively high deformation of 100% to 300%. Coarse-grained titanium alloys are used in the hot die forging of automobile wheel hubs. Two-phase (α+β) titanium alloys with flaky (Widmandelsteiner) microstructure have initial broken grains. β-phase about 250 μkm, α-phase flakes The average length is about 21 μkm and the thickness is about 2 μkm. This example simulates the process and analyzes the obtained results, demonstrating the feasibility of approximate superplasticity techniques. 거친 입자 초가소성 단조 티타늄 합금 자동차 휠 성형 공정 시뮬레이션(그림 14 참조) 단순화를 위해 모든 공정 시뮬레이션은 등온(T=900℃), 접촉면의 마찰 계수는 0.5로 동일하고 유리 윤활제를 사용한다고 가정합니다. 고급 자동차 휠 허브를 위한 거친 입자 초가소성 성형 단계.
TC4 림에 대한 성긴 블랭크의 변형 결과
From the standpoint of rim deformation, 3 -step die forging is still feasible (Fig. 16). It is not difficult to see that at the end of the third step, the cumulative plastic deformation of this part is 300% to 400%, in some places it exceeds 450%, and in some points, it even exceeds 500%. Although the deformation results showed that the microstructure uniformly changed to 30 to 35 μkm at the end of the second step and to 20 to 25 μkm at the end of the third step, the tensile elongation of the specimen with such a microstructure unexpectedly reached δ=400 %~500%. 대상 시뮬레이션은 단조의 모든 심한 변형 영역에서 단조의 평균 응력이 음수(정수압 압축 조건에서), 즉 균열 소스 또는 기공이 제거되고 성능이 극도로 높다는 것을 보여줄 수 있습니다. 높은.
저온 초가소성
최신 항공기 엔진 팬과 컴프레서 블레이드는 부분적으로 탄소 섬유로 만들어집니다. 구조적 강도와 신뢰성을 확보한 상태에서 무게를 줄였기 때문에 티타늄합금 블레이드와 비교하여 높은 경쟁력을 가지고 있습니다. 그러나 탄소 섬유 블레이드의 가장 큰 약점은 충격 인성이 너무 낮다는 것입니다. 사용 과정에서 앞 가장자리는 모래, 자갈 및 새에 부딪혀 항공기 충돌 및 사망의 주요 사고를 일으킬 수 있습니다. 이 난해한 문제를 해결하기 위해 블레이드의 앞쪽 가장자리는 고정 부품이나 접착제를 사용하여 고강도 티타늄 합금 보호 커버로 덮여 있습니다. 그러나 티타늄 합금 부츠의 제조는 부츠가 얇은 벽과 강화되고 무거운 선단 단면을 포함하여 다양한 단면을 가지고 있기 때문에 매우 복잡한 주제입니다. 또한, 외피는 수평 방향의 곡선 형태와 수직 평면 곡률을 포함하는 복잡한 공간 형태를 갖는다.
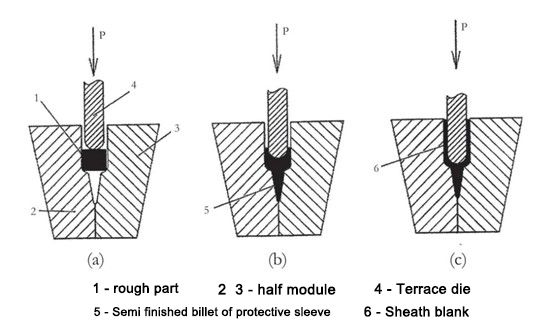
American Nonferrous Gas Turbine Corporation(Chromаlloy Gаs Turbine Corporation USА)은 티타늄 합금 Ti-6Аl-4V 3차원 블랭크를 설계 및 사용하여 외장을 제조했습니다. 블랭크를 밀링하여 내부 V형 포켓을 만듭니다. 측벽은 최종 가공 전에 다이에서 압출됩니다. 압출온도는 850~900 ℃, 표면 가스는 보호 가스 없이 포화 상태입니다. 부품의 벽 두께는 0.2~0.5mm에 불과하며 제조에는 매우 어려운 가공이 필요합니다. 2018년 11월 27일, "2018(제11회) 국제 자동차 기술 연례 회의 및 '자동차 기술 혁신상 시상식'이 상하이에서 성대하게 개최되었습니다. 2018(제11회) 국제 자동차 기술 연례 회의는 신에너지 자동차, 에너지 관리, 자율 주행, 지능형 네트워킹, 경량 및 기타 산업 핫스팟에 중점을 두고 전문적인 기술 교류를 수행하고 첨단 기술 공유 플랫폼을 구축하는 것을 목표로 합니다. "자동차 기술 혁신상" 시상식은 자동차 및 부품 산업에서 첨단 기술의 창시자 및 촉진자를 표창하는 것을 목표로 합니다. 연설 전문가, 국내외 자동차 OEM 및 자동차 부품 공급업체, 대학 연구 기관 대표, 협회 및 정부 기관 대표, 미디어 대표가 400명 이상의 손님과 심도 있는 전문 기술 교류를 진행했으며 더 나은 발전을 함께 기대했습니다. 여행을 위한 미래.
굽힘은 공압출 후에 이루어져야 합니다(그림 18).
복합 압출의 여러 단계에서 공정 단계 제안된 복합 압출 공정의 타당성을 검증하기 위해 디지털 시뮬레이션 방법을 사용하였다. 시뮬레이션 프로세스는 소프트웨어 Deform 3D를 사용하여 설정되었으며 다음과 같은 기본 가정을 사용하여 모델이 설정되었습니다.
- 원본 블랭크는 98000개의 유한 요소로 나뉩니다.
- 강체로서의 금형;
——The movement speed of the punch is 0.5mm/min;
——The friction between the blank and the mold is set to Coulomb friction, μ=0.2;
——Metal flow under isothermal conditions, blank temperature = 650 ℃;
- 블랭크의 이방성 또는 재결정화는 성형 공정 중에 고려되지 않습니다.
그림 18 굽힘 단계 스케치
The initial size of the blank: is 5mm × 10mm × 270mm. It is confirmed that the blank material adopts the titanium alloy Ti-6Аl-4V with rheological characteristics collected from this database.
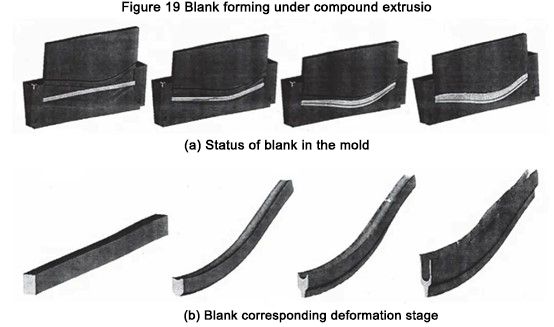
그림 19는 금형에서 변형될 때 블랭크의 상태와 해당 스테이지 형성 이미지를 보여줍니다.

그림 19 컴파운드 압출 하의 블랭크 성형n
The simulation results show that the proposed process is feasible, the wall is formed uniformly, and the logarithmic deformation degree at the wall reaches e ≈ 3. The recommended process is effective at temperatures not exceeding 700°C, which reduces the cost of manufacturing mold parts.
We know that titanium alloys including TC4 (Ti-6Аl-4V) in the ultrafine grain state affect the low-temperature superplasticity effect. The preparation of the ultra-fine grain structure of the blank includes the use of a bar with a diameter of φ70mm, changing the axial load, upsetting several times under the condition of gradually reducing the temperature, and then rolling at 600 °C to a thickness of 5mm. The degree of logarithmic deformation e ≈ 3. Deformation results The average grain size is 0.5 μm (Figure 20).
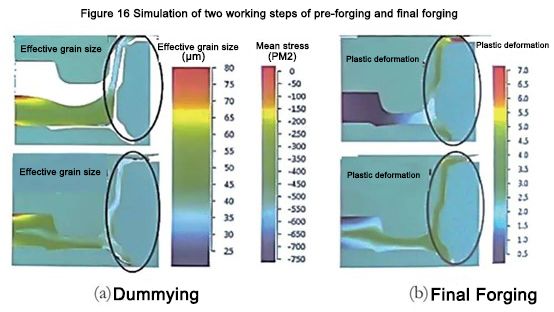
그림 20 블랭크의 미세구조
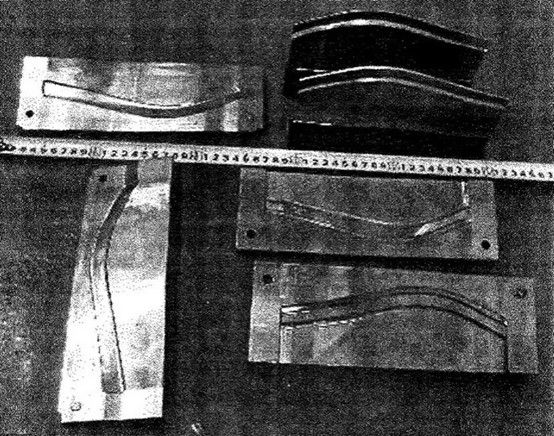
제안된 티타늄 합금 온도는 650 ~ 950 ℃, 압력 처리 공정은 다음과 같은 재료 라벨 코팅을 채택합니다. 원래 블랭크 1에 FR-6 유리 윤활제를 적용합니다. 이러한 코팅은 산화 및 가스 포화를 방지하고 아르곤 가공의 의도된 기계적 특성을 달성합니다. 따라서 블랭크가 다이와 접촉하는 압출 공정에서 윤활재로 코팅을 적용하는 것이 좋습니다. Sheath의 형상은 수평면에 곡선이 있고 수직면에 굴곡이 있으며 압출 전에 해당 평면에서 곧게 펴야 합니다. 주어진 수평면의 조건 하에서 블랭크는 압출을 위해 다이의 두 반쪽에 놓입니다. 다이 반쪽을 닫아 블랭크를 원하는 모양으로 만들고 정방향 및 역방향 압출을 위해 U자형 펀치를 사용합니다. 그런 다음 V 자형 펀치로 굽힘 단계를 구현하도록 금형을 변경하십시오. All forming processes are completed on a CNC isothermal forging hydraulic press, and its main technical parameters are: the nominal force of 25MN, with a pressure of 680kN, completed at 650°C, and a deformation speed of 0.5mm/min. The mold material is tool steel 5Cr3W3MoVSi, and the mold is shown in Figure 21. 복합 압출 후 단조품은 도면 요구 사항을 충족합니다. 외관상 폴딩 및 샌드위치 불량이 없습니다. 시뮬레이션 중에 벽 왜곡이 관찰되지 않았습니다. 가공된 부품은 그림 22에 나와 있습니다. The original structure of the blank is severely deformed (e ≈ 3), which makes it have an ultra-fine grain structure and reduces the process temperature. The microstructure of the sample cut from the wall and front of the sheath is shown in Figure 23. The average grain size of the forgings was determined to be 0.3-0.5μm by a semi-transparent electron microscope. The grain size was reduced to 0.3 μm, and the metal of the wall was severely plastically deformed under the condition of back extrusion. The energy is stored and the grain size is reduced so that the strength of the material is increased by 20% to 30%, and various performance indicators meet the actual requirements. The simulation and test results prove that the trial mass production of sheath parts can be implemented.