近似超塑性技术
The research on the superplasticity of the microcrystalline material structure (the average size of the grains usually does not exceed 10 ~ 20μm) is at elevated temperatures and relatively low deformation speed (usually 10-4 ~ 10-3s-1) ongoing. In fact, it has been determined that any polycrystalline material, including industrial alloys such as aluminum-based, titanium-based, and nickel-based, can be transformed into a superplastic state. In many cases, the use of superplasticity in metal pressure processing can ensure lower deformation forces, reduce the number of process steps, and improve the mechanical properties and dimensional accuracy of semi-finished products. Under conventional forging conditions, the forging temperature range of these metal materials is relatively narrow, especially when rolling thin plates, high ribs, and thin-walled parts, the heat of the billet is quickly absorbed by the tool, and the temperature drops rapidly. Not only does it need to greatly increase the tonnage of the equipment, but it is also easy to cause cracking of the tooling. Especially titanium alloy is more obvious, it is very sensitive to deformation temperature, when the deformation temperature drops from 920 ℃ 至 820 ℃,变形抗力几乎翻了一番。钛合金的超塑性变形力仅为普通轧制的1/30~1/10左右。 钛合金广泛应用于许多工业领域,包括航空航天、汽车和生物医学。众所周知,很多钛合金在供货状态下塑性低,组织不均匀。因此,利用这些材料获得价廉物美的复杂零件具有迫切的现实意义。解决这一问题的有效方法之一是采用超塑性技术。不幸的是,在各种合金中生产超细晶粒既困难又昂贵。
粗粒超塑性
OIВyly а, Р.L.Вlekvell (Strаthсyde, 英国斯特拉斯克莱德格拉斯哥大学), Р.А.Васин (俄罗斯马里国立大学机械工程学院), MKSаrаndzhi (印度技术教育与研究学院)合作关于粗晶超塑性的研究。 超塑性压制成型的主要优点之一是材料可以实现非常大的变形。然而,许多工艺不需要100%到200%的变形。一般金属锻造比达到5,即变形量达到75%。为了确保零件的高适用性,并不总是需要最佳。此外,粗层状微观结构对疲劳裂纹扩展具有更好的稳定性。 In order to obtain high-quality blanks, rough-grained material blanks are first used, whose microstructure cannot guarantee the typical superplastic grain boundary slip deformation mechanism. Under this condition, since the sensitivity to deformation rate is lower than the material superplastic condition, the material can be deformed and softened, and the microstructure can be transformed during deformation. Experimental studies have pointed out that this process can be called approximate superplastic deformation, and some parts of the grain are broken, which can reach a relatively high deformation of 100% to 300%. Coarse-grained titanium alloys are used in the hot die forging of automobile wheel hubs. Two-phase (α+β) titanium alloys with flaky (Widmandelsteiner) microstructure have initial broken grains. β-phase about 250 μkm, α-phase flakes The average length is about 21 μkm and the thickness is about 2 μkm. This example simulates the process and analyzes the obtained results, demonstrating the feasibility of approximate superplasticity techniques. 粗晶超塑性锻造钛合金汽车轮毂成形工艺模拟,如图14所示,为简单起见,所有工艺模拟均采用等温(T=900℃), 接触面具有相同的摩擦系数 0.5, 并假设使用玻璃润滑剂。 高档汽车轮毂粗晶粒超塑性成形步骤。
TC4轮辋粗晶粒变形结果
From the standpoint of rim deformation, 3 -step die forging is still feasible (Fig. 16). It is not difficult to see that at the end of the third step, the cumulative plastic deformation of this part is 300% to 400%, in some places it exceeds 450%, and in some points, it even exceeds 500%. Although the deformation results showed that the microstructure uniformly changed to 30 to 35 μkm at the end of the second step and to 20 to 25 μkm at the end of the third step, the tensile elongation of the specimen with such a microstructure unexpectedly reached δ=400 %~500%。课题模拟可以看出,在锻件的所有严重变形区域,锻件的平均应力为负值(在静水压缩条件下),即消除了裂纹源或气孔,性能极佳高的。
低温超塑性
现代飞机发动机风扇和压缩机叶片部分由碳纤维制成。由于在保证结构强度和可靠性的情况下减轻了重量,与钛合金叶片相比具有很强的竞争力。然而,碳纤维叶片最大的弱点是冲击韧性太低。在使用过程中,前缘被沙子、碎石、飞鸟撞击,会造成飞机坠毁和死亡的重大事故。为了解决这个棘手的问题,叶片前缘通过固定件或胶水的方式覆盖了高强度钛合金保护罩。但是钛合金防尘罩的制造是一个非常复杂的课题,因为防尘罩有不同的横截面,包括薄壁和加强的、重的前缘横截面。此外,护套具有复杂的空间形状,包括水平方向的弯曲形状和垂直平面曲率。
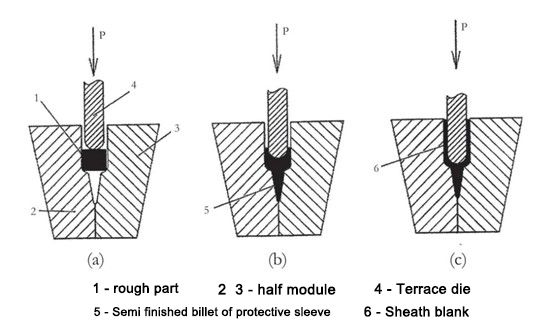
美国有色燃气轮机公司(Chromalloy Gаs Turbine Corporation USА)设计并使用钛合金Ti-6Аl-4V三维毛坯制造护套。坯料经过铣削以创建一个内部 V 形口袋。然后在最终机加工之前在模具中挤压侧壁。挤出温度850~900 ℃, 表面气体在没有保护气体的情况下饱和。零件的壁厚只有0.2~0.5mm,加工难度很大。 2018年11月27日,“2018(第十一届)国际汽车技术年会暨‘汽车技术创新大奖颁奖典礼’”在上海隆重举行。 2018(第十一届)国际汽车技术年会聚焦新能源汽车、能源管理、自动驾驶、智能网联、轻量化等行业热点,旨在开展专业技术交流,搭建前沿技术共享平台。 “汽车技术创新奖”颁奖典礼旨在表彰汽车及零部件行业先进技术的创造者和推动者。演讲专家、国内外汽车主机厂和零部件供应商、高校科研院所代表、协会和政府机构代表、媒体代表与400多位嘉宾进行了深入的专业技术交流,共同期待更美好的未来旅行的未来。
弯曲应在共挤后进行(图 18)。
复合挤出不同阶段的工艺步骤 为了验证所提出的复合材料挤压工艺的可行性,采用了数字仿真方法。仿真过程使用软件Deform 3D建立,模型建立使用基本假设:
- 原始毛坯被分成98000个有限元;
- 作为刚体的模具;
——The movement speed of the punch is 0.5mm/min;
——The friction between the blank and the mold is set to Coulomb friction, μ=0.2;
——Metal flow under isothermal conditions, blank temperature = 650 ℃;
- 成形过程中未考虑毛坯的各向异性甚至再结晶。
图 18 折弯步骤示意图
The initial size of the blank: is 5mm × 10mm × 270mm. It is confirmed that the blank material adopts the titanium alloy Ti-6Аl-4V with rheological characteristics collected from this database.
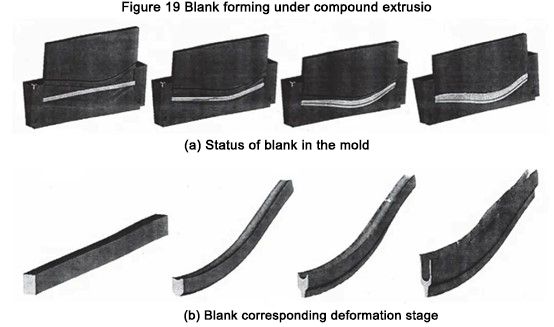
图 19 为坯料在模具中变形时的状态及对应的阶段成型图。

图 19 复合挤压下的毛坯成型n
The simulation results show that the proposed process is feasible, the wall is formed uniformly, and the logarithmic deformation degree at the wall reaches e ≈ 3. The recommended process is effective at temperatures not exceeding 700°C, which reduces the cost of manufacturing mold parts.
We know that titanium alloys including TC4 (Ti-6Аl-4V) in the ultrafine grain state affect the low-temperature superplasticity effect. The preparation of the ultra-fine grain structure of the blank includes the use of a bar with a diameter of φ70mm, changing the axial load, upsetting several times under the condition of gradually reducing the temperature, and then rolling at 600 °C to a thickness of 5mm. The degree of logarithmic deformation e ≈ 3. Deformation results The average grain size is 0.5 μm (Figure 20).
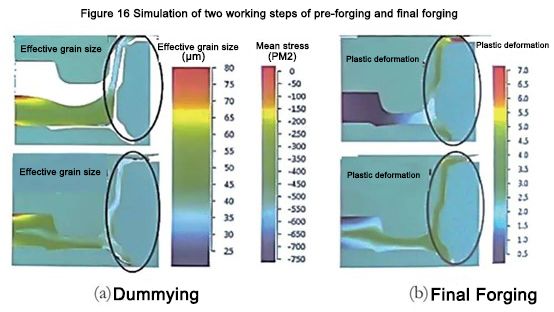
图 20 毛坯的微观结构
建议钛合金温度为650~950 ℃, 压力加工工艺采用如下材料标签涂层:在原坯料1上涂抹FR-6玻璃润滑剂。这些涂层可防止氧化和气体饱和,甚至达到在氩气中加工的预期机械性能。因此,建议在毛坯与模具接触的挤压过程中涂上一层涂层作为润滑材料。 护套的形状在水平面有曲线,在垂直面有弯曲,挤压前需要在相应的平面拉直。在给定水平面的条件下,将毛坯置于两半模具中进行挤压。关闭半模,将毛坯成型为所需形状,并使用 U 形冲头进行正向和反向挤压。然后换模具,用V型冲头实现折弯步骤。 All forming processes are completed on a CNC isothermal forging hydraulic press, and its main technical parameters are: the nominal force of 25MN, with a pressure of 680kN, completed at 650°C, and a deformation speed of 0.5mm/min. The mold material is tool steel 5Cr3W3MoVSi, and the mold is shown in Figure 21. 复合挤压后,锻件达到图纸要求。外观无折叠、夹层缺陷。在模拟过程中,没有观察到壁变形。机加工零件如图 22 所示。 The original structure of the blank is severely deformed (e ≈ 3), which makes it have an ultra-fine grain structure and reduces the process temperature. The microstructure of the sample cut from the wall and front of the sheath is shown in Figure 23. The average grain size of the forgings was determined to be 0.3-0.5μm by a semi-transparent electron microscope. The grain size was reduced to 0.3 μm, and the metal of the wall was severely plastically deformed under the condition of back extrusion. The energy is stored and the grain size is reduced so that the strength of the material is increased by 20% to 30%, and various performance indicators meet the actual requirements. The simulation and test results prove that the trial mass production of sheath parts can be implemented.